Math in Motion — 5 Educators Using Robotics To Teach Math
Posted 04/04/2023 by Harshal S. Chhaya (@hschhaya)
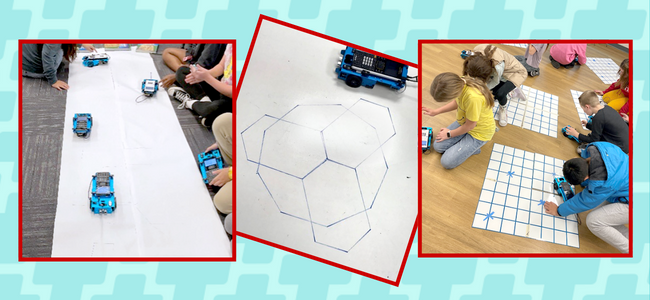
Calling all math teachers out there! April 8–16, 2023, is National Robotics Week (RoboWeek). Are you ready to join in on the fun and inspire your students?
The mission of National Robotics Week is simple: to inspire students in robotics and STEM-related fields and to share the excitement of robotics with audiences of all ages. Texas Instruments can help you, inspire your students, with the TI-Innovator™ Rover (Rover) programmable vehicle. It’s fun, it’s cool, and best of all, students of all ages with no prior coding experience can get the Rover to move and follow their coding commands in just a few minutes!
Let’s take a look at a few specific activities where educators are effectively using the Rover to elevate student understanding and engagement in both math and science.

Activity #1: Students using Rovers in reflections and transformations in geometry
Educator: Michael Hlavacek — Crystal Lake South High School, Crystal Lake, Illinois
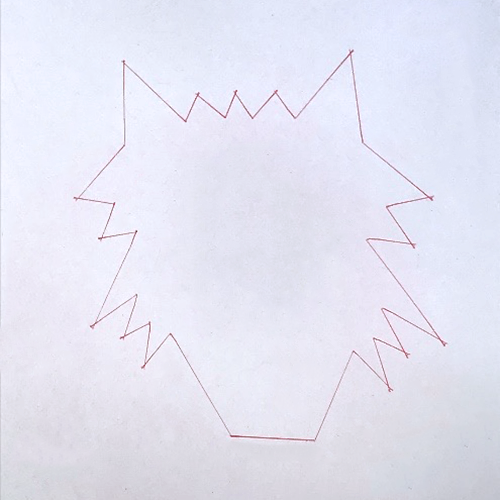
Objective: Students were given a drawing of half of an animal face (example: elephant and wolf), and they had to physically measure the lengths and interior angles of that half-drawn face. They then had to code that to scale on the Rover to recreate the drawing. Finally, to earn full credit, they had to determine how to code in the rest of the face, creating the reflection over the axis of symmetry of the face.
“I believe the lesson allowed students to understand coding a little better, learn to problem-solve, understand a little bit more about the complexity of coding and codes that they encounter through simple things such as their phones.”
Try this with your students:

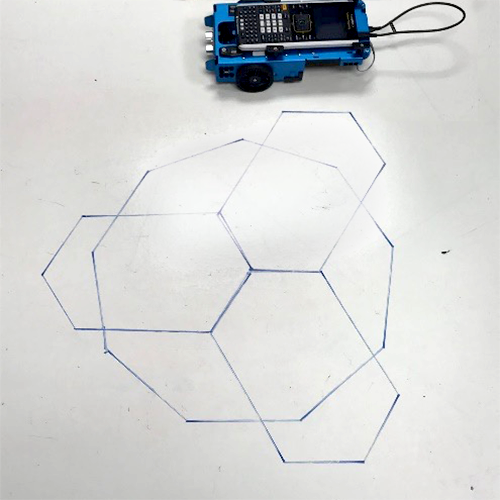
Activity #2: Exploring interior and exterior angles using the Rover
Educator: Casey Gannon — Greenville High School, Greenville, New York
Objective: The Rover can be used to introduce interior and exterior angles by having the students make Rover draw a square and then a triangle. The students pick up very quickly that the 90 degrees for a square is the same inside and outside. However, for drawing a triangle, they need to make the Rover turn the exterior angle.
Students were also challenged to draw a Christmas tree around the winter break. Ms. Gannon even had elementary students (second/third grade) come to work with her class to practice their measuring skills and code the Rover. One of the real values of the Rover is its accessibility to a wide range of ages and abilities! And it was designed specifically for use in education.
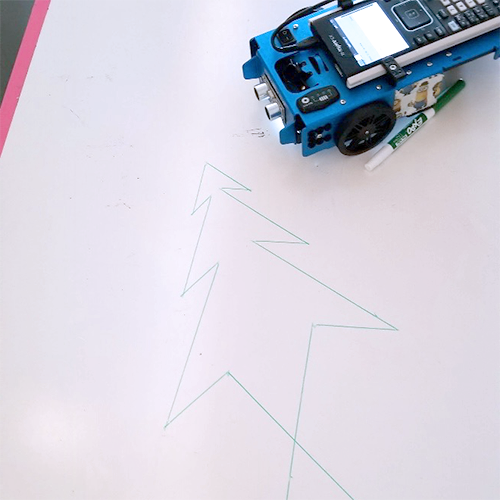

Activities #3 and #4: Coordinate planes, ratio and rates, and music too!
Educator: Susan Reeve — Manlius Pebble Hill School, Syracuse New York
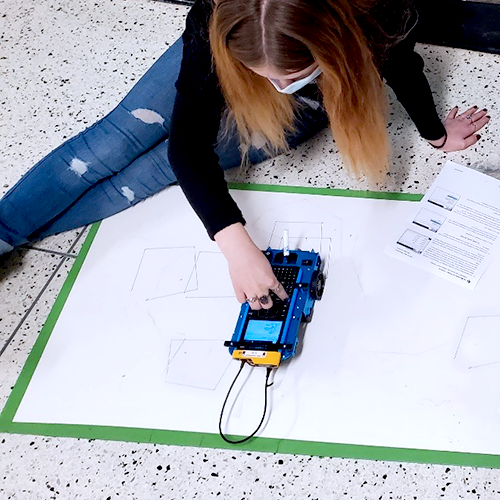
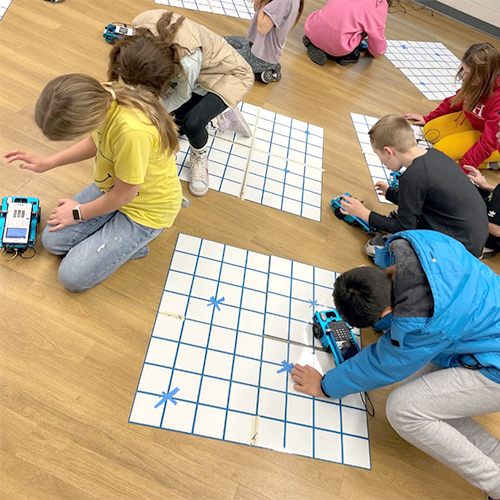
Objective: Students explore graphing in the coordinate plane using Rovers by programming them to find points and objects using different commands such as going forward, left/right and backward.
Here, the Rovers were used for two different “major” activities in Ms. Reeve’s sixth grade math classes. The first is for graphing in the coordinate plane. Without knowing much about the coordinate plane, the students experimented with going forward, left, right and backward.
“The students really benefited from coding and seeing how the Rovers moved to understand the coordinate plane.”

The class then did a lesson on graphing ordered pairs and then used the Rovers to find points and move objects using the coordinates.
After coding in Scratch and using the code to draw polygons, the students then coded the calculators to have the Rovers draw regular polygons on a piece of paper. In the future, Ms. Reeve plans to give students the challenge of drawing a picture with shapes using ordered pairs.
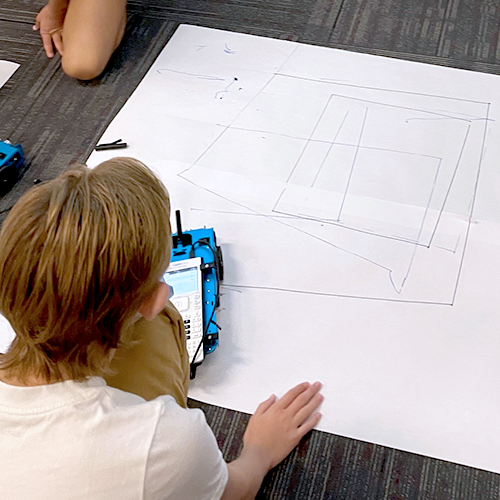
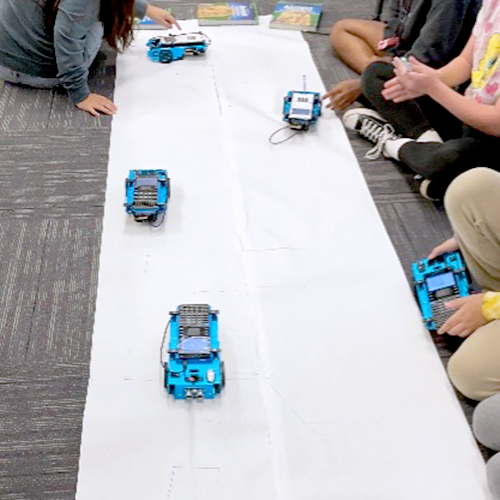
Objective: Exploring ratio and rates unit by using the distance = rate x time activity where students are challenged to try not to hit the animal that is placed randomly on a number line. The students get a great hands-on experience of the value of testing, accuracy, outside things that affect the outcome, and what rate really means.

Students can also use the TI-Innovator™ Hub to code music. Students can see the ratios between the notes and code a song on the calculator that they play on the TI-Innovator™ Hub. What teen or preteen doesn’t love music?
Check out some guided activities on exploring music in TI Minutes of Code (for Python and TI-Innovator™ Technology), Unit 2, Skill Builder 3 and Application activities for either the TI-84 Plus CE or TI-Nspire™ CX II graphing calculator.

Activity #5: Polar coordinates
Educators: Matthew Bennett and Tori Wilson — Mill Creek High School, Hoschton, Georgia
Objective: Students will use the coordinate-based commands to learn about polar coordinates and how to convert between rectangular and polar coordinates. Students are given a program like the one below and they have to write an equivalent program using the polar coordinates. The proof is when Rover’s movements are identical in the two programs.
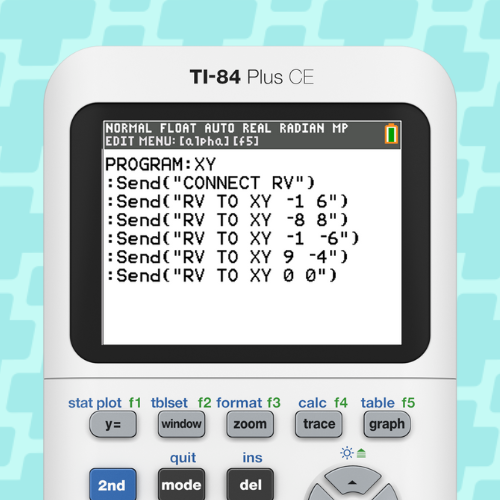
They also use Rover in an activity that connects math to aerospace engineering.
In this case, students choose a real-time orbit from Rogue Space Systems Corporation’s real-time orbital data. They then use their knowledge learned in the math and aerospace engineering unit to create an ellipse formula. That formula can be solved by Rover to draw a scaled orbit on poster paper. The students also learn how to use loops in their code as the Rover steps through their formula to solve for the next location.
Note: Both these activities are part of a ninth grade curriculum in the EPIC program. EPIC is built upon learning strategies that are experiential, project-based, innovative, collaborative and cross-curricular.

Why you should try out the Rover in your classroom:
|
To learn more about Rover and all it can do, visit education.ti.com/en/products/micro-controller/ti-innovator-rover.

Get started using Rover
These are just a handful of examples of how educators are using the Rover and its math-friendly capabilities to help their students understand mathematical ideas.
If you are an educator and want to learn more about robotics, coding and how you can use them in a core subject like math or science, reach out to us at stem-team@ti.com.
- 10 Minutes of Code: Engage students in an easy entry into programming with short activities that help spark interest in coding, computer science and robotics.
- Math in Motion: Students use pre-made programs in these activities that use Rover to teach angle measurements (geometry) and intersection of lines (algebra I).
- Math in Motion Plus: Students write their own programs in these activities for algebra I — the coordinate plane, collinear points, equations of lines — and middle grades (Inequalities, number lines).
There is no better time to bring robotics to your classroom than now, as it is National Robotics Week! Let us help you inspire your students with the Rover. Happy Rover-ing!
About the author: Harshal S. Chhaya is a systems engineer for TI’s educational STEM products. He also leads the company’s robotics outreach programs and works with partners to increase student participation in STEM and robotics competitions. Chhaya enjoys using advanced engineering to make education fun and engaging for students and teachers. He holds 13 patents and was elected by his TI peers as a “Distinguished Member of Technical Staff (Emeritus).”
Tagcloud
Archive
- 2026
- 2025
- 2024
- 2023
- 2022
-
2021
- January (1)
- February (3)
- March (5)
-
April (7)
- Top Tips for Tackling the SAT® with the TI-84 Plus CE
- Monday Night Calculus With Steve Kokoska and Tom Dick
- Which TI Calculator for the SAT® and Why?
- Top Tips From a Math Teacher for Taking the Online AP® Exam
- Celebrate National Robotics Week With Supervised Teardowns
- How To Use the TI-84 Plus Family of Graphing Calculators To Succeed on the ACT®
- AP® Statistics: 6 Math Functions You Must Know for the TI-84 Plus
- May (1)
- June (3)
- July (2)
- August (5)
- September (2)
-
October (4)
- Transformation Graphing — the Families of Functions Modular Video Series to the Rescue!
- Top 3 Halloween-Themed Classroom Activities
- In Honor of National Chemistry Week, 5 “Organic” Ways to Incorporate TI Technology Into Chemistry Class
- 5 Spook-tacular Ways to Bring the Halloween “Spirits” Into Your Classroom
- November (4)
- December (1)
- 2020
- 2019
-
2018
- January (1)
- February (5)
- March (4)
- April (5)
- May (4)
- June (4)
- July (4)
- August (4)
- September (5)
- October (8)
-
November (8)
- Testing Tips: Using Calculators on Class Assessments
- Girls in STEM: A Personal Perspective
- 5 Teachers You Should Be Following on Instagram Right Now
- Meet TI Teacher of the Month: Katie England
- End-of-Marking Period Feedback Is a Two-Way Street
- #NCTMregionals Kansas City 2018 Recap
- Slope: It Shouldn’t Just Be a Formula
- Hit a high note exploring the math behind music
- December (5)
- 2017
- 2016
- 2015
